



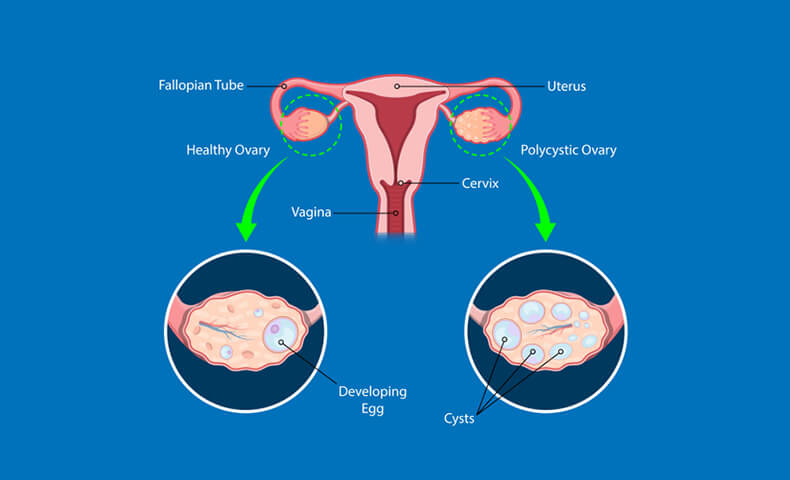
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods or excess male hormone (androgen) levels.
The ovaries may develop numerous small collections of fluid (follicles) and fail to regularly release eggs.The exact cause of PCOS is unknown.
Early diagnosis and treatment along with weight loss may reduce the risk of long-term complications such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Fertility treatment begins with ovulation induction 3-4 months followed by IUI for 2-3 months. If all this fails, IVF is best option for this group of patients.

Thyroid dysfunction is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive years.
Women with hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are at increased risk for infertility and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Uterine or endometrial polyps are overgrowths of the inner lining of the uterus. Women with polyps usually present with irregular or heavy vaginal bleeding. Single or multiple polyps can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in size.
Hysteroscopic removal of polyps under anaesthesia help in improving the chances of conception and pregnancy.
Uterine anomalies are a deviation from the normal genital tract in females, This is a common benign condition ranging from 4-7%, leading to infertility and miscarraige.
Proper/exact diagnosis and expertise treatment helps in achieving pregnancy and a happy family.
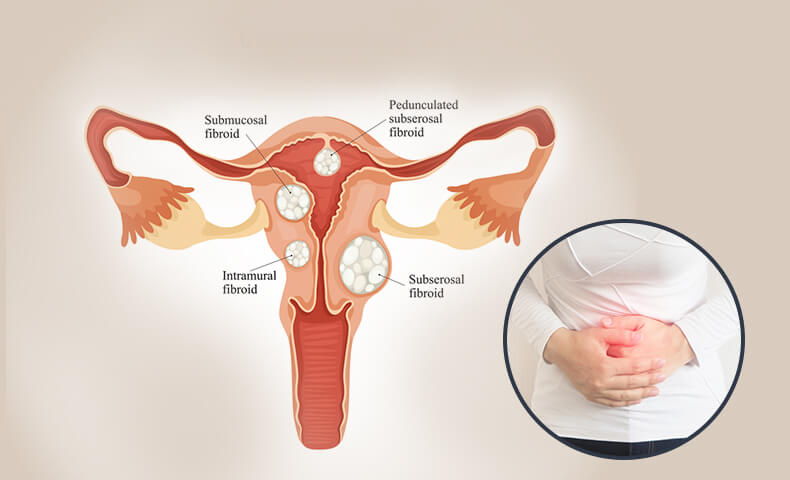
Fibroids are abnormal growths that develop in or on a woman’s uterus. Sometimes these tumors become quite large and cause severe abdominal pain and heavy periods.
In other cases, they cause no signs or symptoms at all. The growths are typically benign, or noncancerous.
Symptoms include :
infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss
Long term medical treatment not indicated.
Surgical treatment is the best option
In women with infertility – myomectomy – laparoscopic/hysteroscopic
In women who had completed their family – laparoscopic hysterectomy
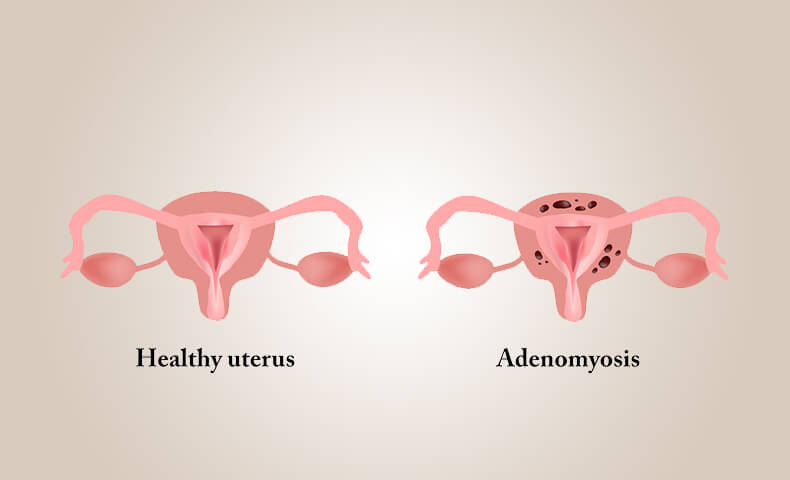
It is a progressive disease & the treatment depends on age, symptoms and severity of disease There is no single treatment that completely cures endometriosis.
Various treatment options include :
Medical (pain killers)
Hormonal therapy
Surgery (laparascopy)
Poor responders represent more than a third of women undergoing assisted reproduction. Typically they are patients with advanced maternal age and low ovarian reserve.
However, there is a younger group that unexpectedly demonstrates impaired response to controlled ovarian hyperstimulation. The etiologies in many of these cases are still unclear.
In our program, the determination of basal cycle day 3 serum FSH, LH and E2 levels, measurement of AMH, and the estimation of the basal antral follicular count by transvaginal ultrasonography, are the preferred screening tests for ovarian reserve in all IVF patients, and together with the woman’s age, determine the ovarian stimulation regimen to be chosen for the cycle treatment.
In spite of a variety of protocols and adjuvant therapies of unproven benefit, these patients have compromised outcomes and continue to represent a challenge to reproductive endocrinologists.

This condition is defined as loss of 2 or more consecutive pregnancies, before the fetus reaches viability. It affects about 1-2% of couples trying to conceive.
Management of these couples is a challenge to the fertility specialist.
Various investigations include :
3D ultrasound
hysteroscopy
karyotyping of couple
thrombophilia screening
anti phospholipid antibody testing
immunological tests are done
Treatment options like genetic counsellimg, low dose aspirin, etc are given based on the diagnosis

Recurrent implantation failure refers to failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after transfer of at least four good-quality embryos in a minimum of three fresh or frozen cycles in a woman under the age of 40 years.
The failure to implant may be a consequence of embryo or uterine factors. Thorough investigations should be carried out to ascertain whether there is any underlying cause of the condition.
Ovarian function should be assessed by measurement of antral follicle count, FSH and anti-Müllerian hormone. Increased sperm DNA fragmentation may be a contributory cause.
Various uterine pathology including fibroids, endometrial polyps, congenital anomalies and intrauterine adhesions should be excluded by ultrasonography and hysteroscopy.
Hydrosalpinges are a recognized cause of implantation failure and should be excluded by hysterosalpingogram if necessary, laparoscopy should be performed to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Treatment offered should be evidence based, aimed at improving embryo quality or endometrial receptivity. Gamete donation or surrogacy may be necessary if there is no realistic chance of success with further IVF attempts.
This is to be considered if you have a serious illness such as cancer, and will potentially cause damage to your eggs/ sperm from chemotherapy, radiotherapy or other treatments, including surgery.
Some women, especially those in a well set career, may also consider fertility preservation because their age is advancing, but they are not ready or able to have a baby right now.
A detailed discussion with the doctor regarding the situation, as well as your motivations, i.e. planned medical treatments or an intentional delay in commencing a family.
For young women, these options include freezing of eggs, freezing of embryos, freezing of ovarian tissue, and medications which may protect the ovaries from toxic chemotherapy drugs.
For young men the options include freezing sperm and freezing of testicular tissue.
